Welcome to CARE (Cardiac Atlas of Regulatory Elements) Portal¶
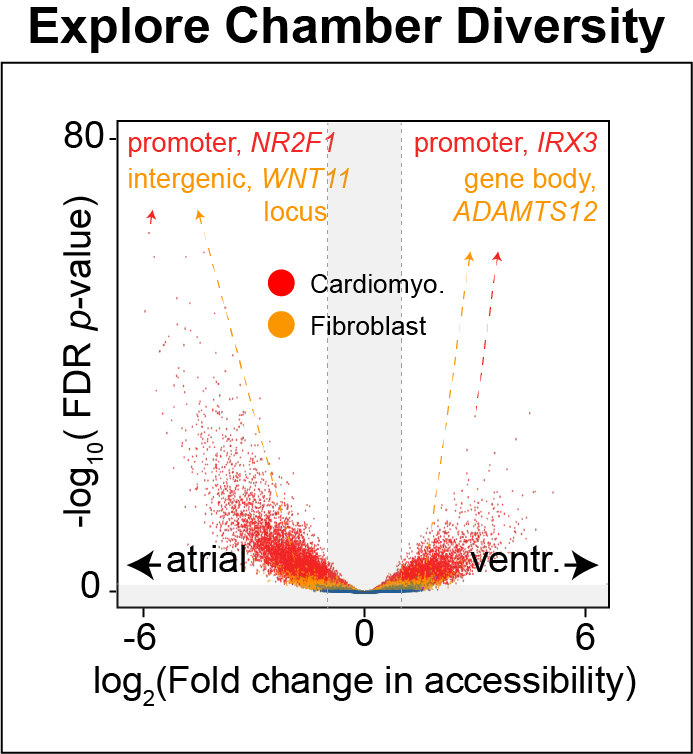
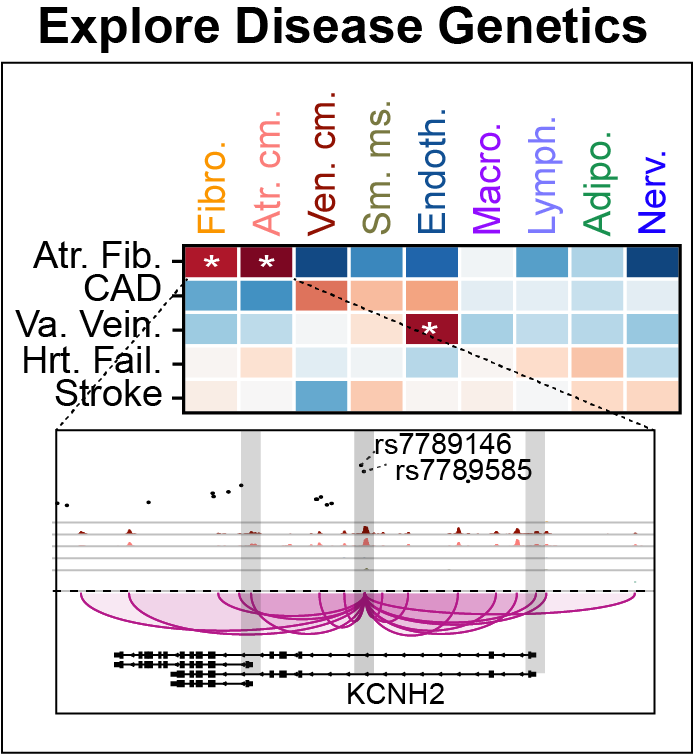
See also
Interactive single-cell browsers are available here http://ns104190.ip-147-135-44.us/data_CARE_portal/snATAC/ucsc_browser/ and genome browser tracks can be accessed here http://ns104190.ip-147-135-44.us/data_CARE_portal/snATAC/IGV/IGV_chamber_bigwig.html
About the Cardiac Atlas of Regulatory Elements project¶
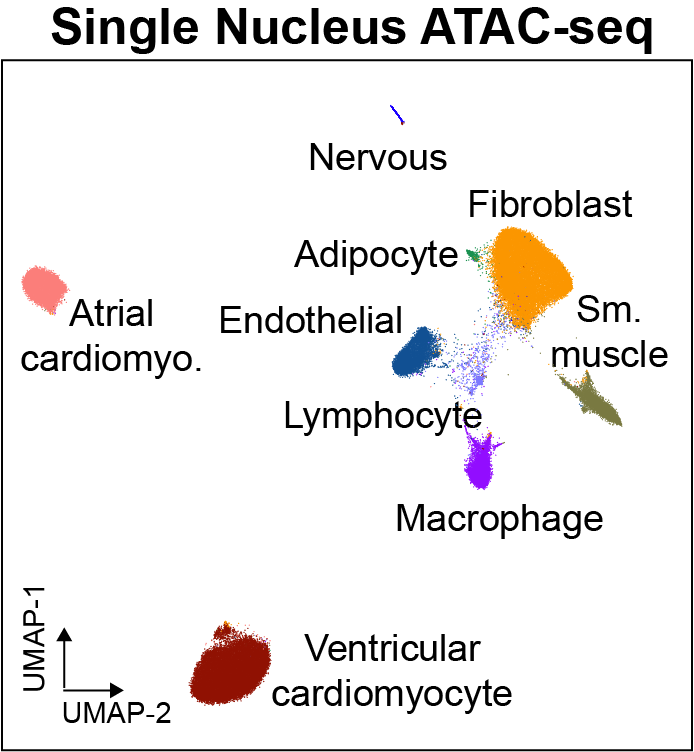
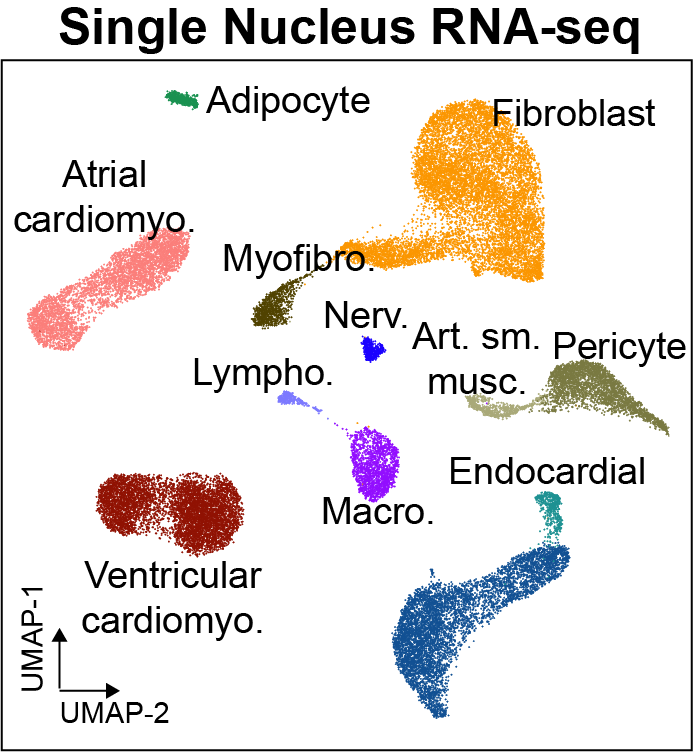
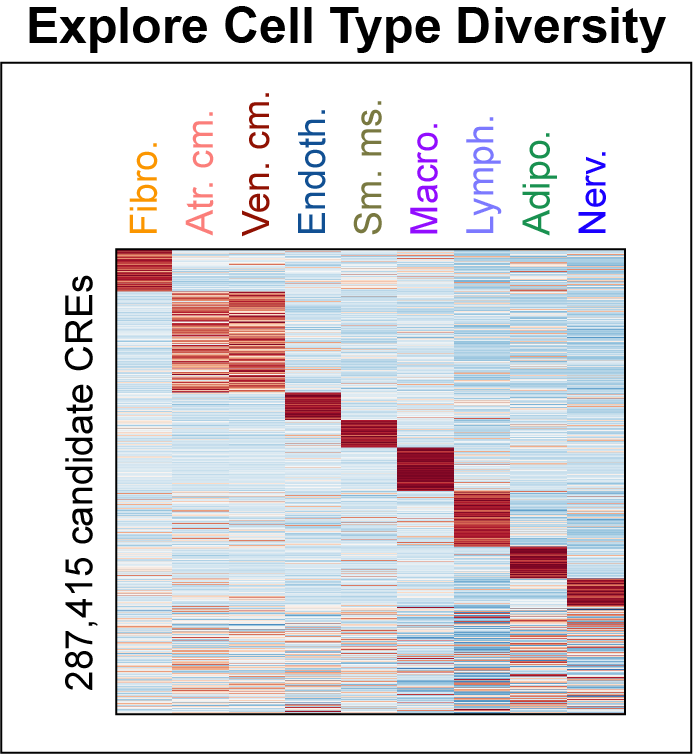
Cis-regulatory elements such as enhancers and promoters control gene expression patterns in the human heart. Dysregulation of these elements can result in many cardiovascular diseases that are major leading causes of morbidity and mortality worldwide. In addition, genetic variants associated with cardiovascular disease risk are enriched within cis-regulatory elements. However, the location and activity of these cis-regulatory elements in individual cardiac cell types remains to be fully defined. We performed single nucleus ATAC-seq and single nucleus RNA-seq to define a catalogue of candidate >287,000 cis-regulatory elements (cCREs) and gene expression patterns for the distinct cell types comprising each chamber of non-failing human hearts and revealed gene regulatory programs controlling specific cell types in a cardiac region/structure-dependent manner. We further report enrichment of cardiovascular disease risk variants in cCREs of distinct cardiac cell types, including a strong enrichment of atrial fibrillation variants in cardiomyocyte cCREs and uncovered the functional impact of atrial fibrillation risk variants in a cardiomyocyte-specific enhancer which regulated KCNH2/HERG expression. In summary, this comprehensive atlas of human cardiac cCREs will facilitate the analyses of cell type-specific gene regulatory programs and interpretation of genetic risk loci for a wide spectrum of cardiovascular diseases.
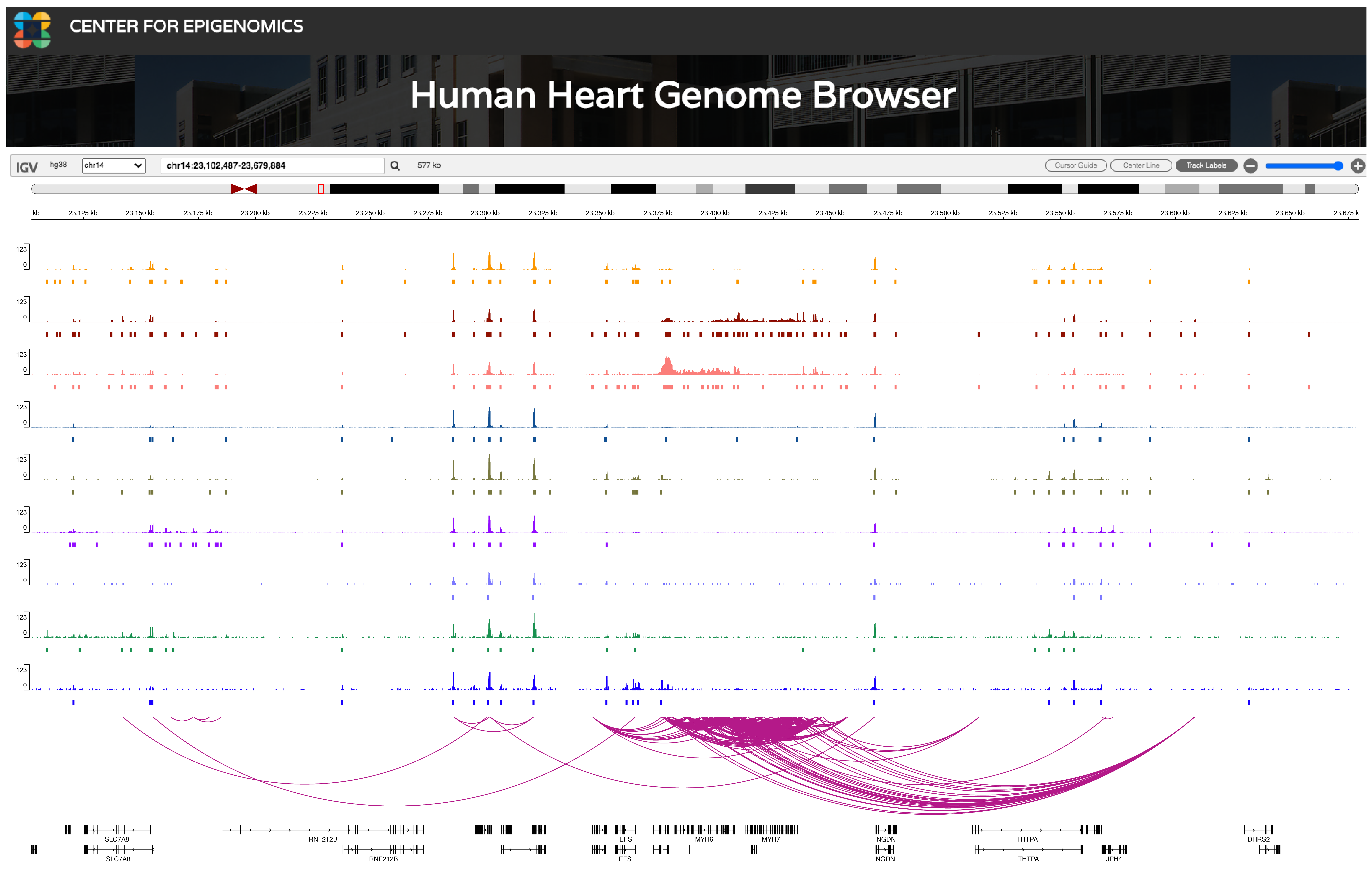
We provide an interactive genome browser for snATAC-seq. We also provide interactive single cell browsers for snRNA datasets, snATAC-seq datasets, and transcription factor motif enrichment.
Specific download links¶
We provide two tables specific to snATAC-Seq for download:
http://ns104190.ip-147-135-44.us/data_CARE_portal/snATAC/matrices/Supplemental_Table_5_RAS.tsv “Matrix displays relative accessibility scores (RAS) for individual clusters for each peak in the union set of peaks
http://ns104190.ip-147-135-44.us/data_CARE_portal/snATAC/matrices/Supplemental_Table_5_RPKM.tsv displays reads per kilobase per million mapped reads (RPKM) for individual clusters for each peak in the union set of peaks
Citations¶
James D Hocker, Olivier B Poirion#, Fugui Zhu#, Justin Buchanan, Kai Zhang, Joshua Chiou, Tsui-Min Wang, Xiaomeng Hou, Yang Eric Li, Yanxiao Zhang, Elie Farah, Allen Wang, Andrew D McCulloch, Kyle J Gaulton, Bing Ren*, Neil C Chi*, Sebastian Preissl*. Cardiac Cell Type-Specific Gene Regulatory Programs and Disease Risk Association. bioRxiv 2020.09.11.291724; doi: https://doi.org/10.1101/2020.09.11.291724 #contributed equally, *corresponding authors
Contacts¶
Olivier Poirion opoirion@health.ucsd.edu
James Hocker jhocker@health.ucsd.edu
Sebastian Preissl spreissl@health.ucsd.edu